|

|
Carter, who has rarely used his full nameJames Earl Carter, Jr. was born October 1, 1924, in Plains, Georgia. Peanut farming, talk of politics, and devotion to the Baptist faith were mainstays of his upbringing. Upon graduation in 1946 from the Naval Academy in Annapolis, Maryland, Carter married Rosalynn Smith. The Carters have three sons, John William (Jack), James Earl III (Chip), Donnel Jeffrey (Jeff), and a daughter, Amy Lynn. After seven years' service as a naval officer, Carter returned to Plains. In 1962 he entered state politics, and eight years later he was elected Governor of Georgia. Among the new young southern governors, he attracted attention by emphasizing ecology, efficiency in government, and the removal of racial barriers.
Carter announced his candidacy for President in December 1974 and began a two-year campaign that gradually gained momentum. At the Democratic Convention, he was nominated on the first ballot. He chose Senator Walter F. Mondale of Minnesota as his running mate. Carter campaigned hard against President Gerald R. Ford, debating with him three times. Carter won by 297 electoral votes to 241 for Ford.
Carter worked hard to combat the continuing economic woes of inflation and unemployment. By the end of his administration, he could claim an increase of nearly eight million jobs and a decrease in the budget deficit, measured in percentage of the gross national product. Unfortunately, inflation and interest rates were at near record highs, and efforts to reduce them caused a short recession. Carter could point to a number of achievements in domestic affairs. He dealt with the energy shortage by establishing a national energy policy and by decontrolling domestic petroleum prices to stimulate production. He prompted Government efficiency through civil service reform and proceeded with deregulation of the trucking and airline industries. He sought to improve the environment. His expansion of the national park system included protection of 103 million acres of Alaskan lands. To increase human and social services, he created the Department of Education, bolstered the Social Security system, and appointed record numbers of women, blacks, and Hispanics to Government jobs.
In foreign affairs, Carter set his own style. His championing of human rights was coldly received by the Soviet Union and some other nations. In the Middle East, through the Camp David agreement of 1978, he helped bring amity between Egypt and Israel. He succeeded in obtaining ratification of the Panama Canal treaties. Building upon the work of predecessors, he established full diplomatic relations with the People's Republic of China and completed negotiation of the SALT II nuclear limitation treaty with the Soviet Union.
There were serious setbacks, however. The Soviet invasion of Afghanistan caused the suspension of plans for ratification of the SALT II pact. The seizure as hostages of the U. S. embassy staff in Iran dominated the news during the last 14 months of the administration. The consequences of Iran's holding Americans captive, together with continuing inflation at home, contributed to Carter's defeat in 1980. Even then, he continued the difficult negotiations over the hostages. Iran finally released the 52 Americans the same day Carter left office.

|
One of nine children of a Presbyterian minister, Cleveland was born in New Jersey in 1837. He was raised in upstate New York. As a lawyer in Buffalo, he became notable for his single-minded concentration upon whatever task faced him.
At 44, he emerged into a political prominence that carried him to the White House in three years. Running as a reformer, he was elected Mayor of Buffalo in 1881, and later, Governor of New York.
Cleveland won the Presidency with the combined support of Democrats and reform Republicans, the "Mugwumps," who disliked the record of his opponent James G. Blaine of Maine.
A bachelor, Cleveland was ill at ease at first with all the comforts of the White House. "I must go to dinner," he wrote a friend, "but I wish it was to eat a pickled herring a Swiss cheese and a chop at Louis' instead of the French stuff I shall find." In June 1886 Cleveland married 21-year-old Frances Folsom; he was the only President married in the White House.
Cleveland vigorously pursued a policy barring special favors to any economic group. Vetoing a bill to appropriate $10,000 to distribute seed grain among drought-stricken farmers in Texas, he wrote: "Federal aid in such cases encourages the expectation of paternal care on the part of the Government and weakens the sturdiness of our national character. . . . " He also vetoed many private pension bills to Civil War veterans whose claims were fraudulent. When Congress, pressured by the Grand Army of the Republic, passed a bill granting pensions for disabilities not caused by military service, Cleveland vetoed it, too.
He angered the railroads by ordering an investigation of western lands they held by Government grant. He forced them to return 81,000,000 acres. He also signed the Interstate Commerce Act, the first law attempting Federal regulation of the railroads.
In December 1887 he called on Congress to reduce high protective tariffs. Told that he had given Republicans an effective issue for the campaign of 1888, he retorted, "What is the use of being elected or re-elected unless you stand for something?" But Cleveland was defeated in 1888; although he won a larger popular majority than the Republican candidate Benjamin Harrison, he received fewer electoral votes.
Elected again in 1892, Cleveland faced an acute depression. He dealt directly with the Treasury crisis rather than with business failures, farm mortgage foreclosures, and unemployment. He obtained repeal of the mildly inflationary Sherman Silver Purchase Act and, with the aid of Wall Street, maintained the Treasury's gold reserve.
When railroad strikers in Chicago violated an injunction, Cleveland sent Federal troops to enforce it. "If it takes the entire army and navy of the United States to deliver a post card in Chicago," he thundered, "that card will be delivered."
Cleveland's blunt treatment of the railroad strikers stirred the pride of many Americans. So did the vigorous way in which he forced Great Britain to accept arbitration of a disputed boundary in Venezuela. But his policies during the depression were generally unpopular. His party deserted him and nominated William Jennings Bryan in 1896. After leaving the White House, Cleveland lived in retirement in Princeton, New Jersey. He died in 1908.

|
After the failure in his second year of a huge program of health care reform, Clinton shifted emphasis, declaring "the era of big government is over." He sought legislation to upgrade education, to protect jobs of parents who must care for sick children, to restrict handgun sales, and to strengthen environmental rules. President Clinton was born William Jefferson Blythe IV on August 19, 1946, in Hope, Arkansas, three months after his father died in a traffic accident. When he was four years old, his mother wed Roger Clinton, of Hot Springs, Arkansas. In high school, he took the family name.
He excelled as a student and as a saxophone player and once considered becoming a professional musician. As a delegate to Boys Nation while in high school, he met President John Kennedy in the White House Rose Garden. The encounter led him to enter a life of public service.
Clinton was graduated from Georgetown University and in 1968 won a Rhodes Scholarship to Oxford University. He received a law degree from Yale University in 1973, and entered politics in Arkansas.
He was defeated in his campaign for Congress in Arkansas's Third District in 1974. The next year he married Hillary Rodham, a graduate of Wellesley College and Yale Law School. In 1980, Chelsea, their only child, was born. Clinton was elected Arkansas Attorney General in 1976, and won the governorship in 1978. After losing a bid for a second term, he regained the office four years later, and served until he defeated incumbent George Bush and third party candidate Ross Perot in the 1992 presidential race.
Clinton and his running mate, Tennessee's Senator Albert Gore Jr., then 44, represented a new generation in American political leadership. For the first time in 12 years both the White House and Congress were held by the same party. But that political edge was brief; the Republicans won both houses of Congress in 1994.
In 1998, as a result of issues surrounding personal indiscretions with a young woman White House intern, Clinton was the second U.S. president to be impeached by the House of Representatives. He was tried in the Senate and found not guilty of the charges brought against him. He apologized to the nation for his actions and continued to have unprecedented popular approval ratings for his job as president.
In the world, he successfully dispatched peace keeping forces to war-torn Bosnia and bombed Iraq when Saddam Hussein stopped United Nations inspections for evidence of nuclear, chemical, and biological weapons. He became a global proponent for an expanded NATO, more open international trade, and a worldwide campaign against drug trafficking. He drew huge crowds when he traveled through South America, Europe, Russia, Africa, and China, advocating U.S. style freedom.

|
Coolidge was "distinguished for character more than for heroic achievement," wrote a Democratic admirer, Alfred E. Smith. "His great task was to restore the dignity and prestige of the Presidency when it had reached the lowest ebb in our history ... in a time of extravagance and waste."
Born in Plymouth, Vermont, on July 4, 1872, Coolidge was the son of a village storekeeper. He was graduated from Amherst College with honors, and entered law and politics in Northampton, Massachusetts. Slowly, methodically, he went up the political ladder from councilman in Northampton to Governor of Massachusetts, as a Republican. En route he became thoroughly conservative.
As President, Coolidge demonstrated his determination to preserve the old moral and economic precepts amid the material prosperity which many Americans were enjoying. He refused to use Federal economic power to check the growing boom or to ameliorate the depressed condition of agriculture and certain industries. His first message to Congress in December 1923 called for isolation in foreign policy, and for tax cuts, economy, and limited aid to farmers.
He rapidly became popular. In 1924, as the beneficiary of what was becoming known as "Coolidge prosperity," he polled more than 54 percent of the popular vote.
In his Inaugural he asserted that the country had achieved "a state of contentment seldom before seen," and pledged himself to maintain the status quo. In subsequent years he twice vetoed farm relief bills, and killed a plan to produce cheap Federal electric power on the Tennessee River.
The political genius of President Coolidge, Walter Lippmann pointed out in 1926, was his talent for effectively doing nothing: "This active inactivity suits the mood and certain of the needs of the country admirably. It suits all the business interests which want to be let alone.... And it suits all those who have become convinced that government in this country has become dangerously complicated and top-heavy...."
Coolidge was both the most negative and remote of Presidents, and the most accessible. He once explained to Bernard Baruch why he often sat silently through interviews: "Well, Baruch, many times I say only 'yes' or 'no' to people. Even that is too much. It winds them up for twenty minutes more."
But no President was kinder in permitting himself to be photographed in Indian war bonnets or cowboy dress, and in greeting a variety of delegations to the White House. Both his dry Yankee wit and his frugality with words became legendary. His wife, Grace Goodhue Coolidge, recounted that a young woman sitting next to Coolidge at a dinner party confided to him she had bet she could get at least three words of conversation from him. Without looking at her he quietly retorted, "You lose." And in 1928, while vacationing in the Black Hills of South Dakota, he issued the most famous of his laconic statements, "I do not choose to run for President in 1928." By the time the disaster of the Great Depression hit the country, Coolidge was in retirement. Before his death in January 1933, he confided to an old friend, ". . . I feel I no longer fit in with these times."
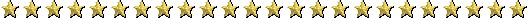
|
Born in Texas in 1890, brought up in Abilene, Kansas, Eisenhower was the third of seven sons. He excelled in sports in high school, and received an appointment to West Point. Stationed in Texas as a second lieutenant, he met Mamie Geneva Doud, whom he married in 1916.
In his early Army career, he excelled in staff assignments, serving under Generals John J. Pershing, Douglas MacArthur, and Walter Krueger. After Pearl Harbor, General George C. Marshall called him to Washington for a war plans assignment. He commanded the Allied Forces landing in North Africa in November 1942; on D-Day, 1944, he was Supreme Commander of the troops invading France.
After the war, he became President of Columbia University, then took leave to assume supreme command over the new NATO forces being assembled in 1951. Republican emissaries to his headquarters near Paris persuaded him to run for President in 1952. "I like Ike" was an irresistible slogan; Eisenhower won a sweeping victory. Negotiating from military strength, he tried to reduce the strains of the Cold War. In 1953, the signing of a truce brought an armed peace along the border of South Korea. The death of Stalin the same year caused shifts in relations with Russia.
New Russian leaders consented to a peace treaty neutralizing Austria. Meanwhile, both Russia and the United States had developed hydrogen bombs. With the threat of such destructive force hanging over the world, Eisenhower, with the leaders of the British, French, and Russian governments, met at Geneva in July 1955.
The President proposed that the United States and Russia exchange blueprints of each other's military establishments and "provide within our countries facilities for aerial photography to the other country." The Russians greeted the proposal with silence, but were so cordial throughout the meetings that tensions relaxed.
Suddenly, in September 1955, Eisenhower suffered a heart attack in Denver, Colorado. After seven weeks he left the hospital, and in February 1956 doctors reported his recovery. In November he was elected for his second term.
In domestic policy the President pursued a middle course, continuing most of the New Deal and Fair Deal programs, emphasizing a balanced budget. As desegregation of schools began, he sent troops into Little Rock, Arkansas, to assure compliance with the orders of a Federal court; he also ordered the complete desegregation of the Armed Forces. "There must be no second class citizens in this country," he wrote.
Eisenhower concentrated on maintaining world peace. He watched with pleasure the development of his "atoms for peace" program--the loan of American uranium to "have not" nations for peaceful purposes. Before he left office in January 1961, for his farm in Gettysburg, he urged the necessity of maintaining an adequate military strength, but cautioned that vast, long-continued military expenditures could breed potential dangers to our way of life. He concluded with a prayer for peace "in the goodness of time." Both themes remained timely and urgent when he died, after a long illness, on March 28, 1969.

|
Born in the Finger Lakes country of New York in 1800, Fillmore as a youth endured the privations of frontier life. He worked on his father's farm, and at 15 was apprenticed to a cloth dresser. He attended one-room schools, and fell in love with the redheaded teacher, Abigail Powers, who later became his wife. In 1823 he was admitted to the bar; seven years later he moved his law practice to Buffalo. As an associate of the Whig politician Thurlow Weed, Fillmore held state office and for eight years was a member of the House of Representatives. In 1848, while Comptroller of New York, he was elected Vice President.
Fillmore presided over the Senate during the months of nerve-wracking debates over the Compromise of 1850. He made no public comment on the merits of the compromise proposals, but a few days before President Taylor's death, he intimated to him that if there should be a tie vote on Henry Clay's bill, he would vote in favor of it.
Thus the sudden accession of Fillmore to the Presidency in July 1850 brought an abrupt political shift in the administration. Taylor's Cabinet resigned and President Fillmore at once appointed Daniel Webster to be Secretary of State, thus proclaiming his alliance with the moderate Whigs who favored the Compromise.
A bill to admit California still aroused all the violent arguments for and against the extension of slavery, without any progress toward settling the major issues. Clay, exhausted, left Washington to recuperate, throwing leadership upon Senator Stephen A. Douglas of Illinois. At this critical juncture, President Fillmore announced in favor of the Compromise. On August 6, 1850, he sent a message to Congress recommending that Texas be paid to abandon her claims to part of New Mexico.
This helped influence a critical number of northern Whigs in Congress away from their insistence upon the Wilmot Proviso--the stipulation that all land gained by the Mexican War must be closed to slavery. Douglas's effective strategy in Congress combined with Fillmore's pressure from the White House to give impetus to the Compromise movement. Breaking up Clay's single legislative package, Douglas presented five separate bills to the Senate:
Admit California as a free state.
Settle the Texas boundary and compensate her.
Grant territorial status to New Mexico.
Place Federal officers at the disposal of slaveholders seeking fugitives.
Abolish the slave trade in the District of Columbia.
Each measure obtained a majority, and by September 20, President Fillmore had signed them into law. Webster wrote, "I can now sleep of nights."
Some of the more militant northern Whigs remained irreconcilable, refusing to forgive Fillmore for having signed the Fugitive Slave Act. They helped deprive him of the Presidential nomination in 1852.
Within a few years it was apparent that although the Compromise had been intended to settle the slavery controversy, it served rather as an uneasy sectional truce. As the Whig Party disintegrated in the 1850's, Fillmore refused to join the Republican Party; but, instead, in 1856 accepted the nomination for President of the Know Nothing, or American, Party. Throughout the Civil War he opposed President Lincoln and during Reconstruction supported President Johnson. He died in 1874.